The water solution at room temperature is 69%, and can be converted into the structure of epoxidation immediately under alkaline condition.
Indicator:
Item
Result
Appreance
Colorless liquid
content% ≥
69
1,3-dichloropropanol ppm ≤
10
Epichlorohydrin ppm ≤
5
PH value
4-7
Solubility
Soluble in water and 2- alcohol
Advantage:
The product appearance is transparent liquid, colorless and tasteless, the impurity content is low, is less than 10ppm.
Because the use of continuous production process, product quality is stability;
The product response rate is higher than 90%.
Application area
1) paper industry
Mainly as a liquid cationic etherifying agent, widely used in fiber, cellulose derivatives and starch modified; as paper internal application of adhesive, filler and fine fiber interception of additives.
(2) textile industry
Liquid cationic etherifying agent react whit cotton fiber, improve the dye binding; reacts with starch obtained cationic starch, as the sizing agent.
(3) water treatment industry
Suspended matters in water is negatively charged, react whit liquid cationic etherifying agent,produce cationic polymer as flocculants are widely used in water purification.
(4) chemical industry for daily use
The reaction of aqueous cationic etherifying agent create cationic guar gum are important chemicals.
3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride 3-Chloro-2-Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride,69% 3-Chloro-2-Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride,65% 3-Chloro-2-Hydroxypropyltrimethyl Ammonium Chloride Shandong Tiancheng Chemical Co., Ltd. , https://www.akdchemical.nl
Smart locks, wireless transmission protocols commonly used in the smart home field, current wired and wireless Internet, 2G and 3G networks, etc., can be used as part of the transport layer. In the future where IoT terminals such as smart communities and smart homes are popular, in order to ensure the security of wireless transmission data, wireless transmission protocols are particularly important. 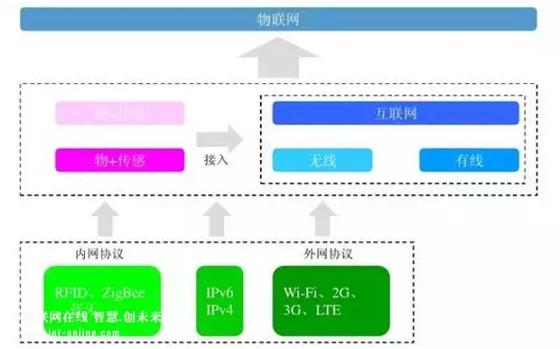
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), commonly known as electronic tags. It is a non-contact automatic identification technology that automatically identifies target objects and acquires relevant data through RF signals.
RFID consists of three basic elements: Tag, Reader and Antenna. The basic working principle of RFID technology is not complicated. After the tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the RF signal from the reader and sends the product information (Passive Tag, Passive Tag or Passive Tag) stored in the chip by the energy obtained by the induced current. Or actively send a signal of a certain frequency (Active Tag, active tag or active tag), the reader reads the information and decodes it, and sends it to the central information system for data processing. 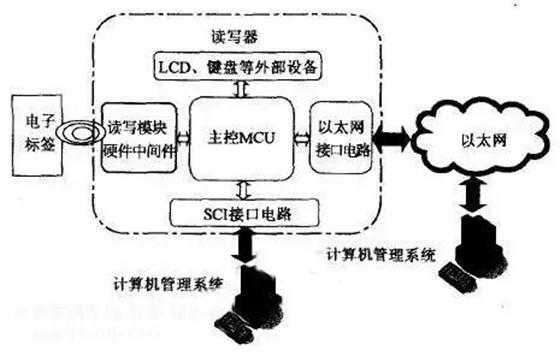
Infrared infrared technology is also a kind of wireless communication technology, which can transmit wireless data. Infrared has obvious features: point-to-point transmission, wireless, can not be too far away, to align the direction, can not penetrate the wall and obstacles, almost impossible to control the progress of information transmission. In addition to the 2.4 GHz frequency, the 802.11 physical layer standard also includes infrared related standards. IrDA 1.0 supports communication rates up to 115.2 kbps and IrDA 1.1 supports up to 4 Mbps. The technology has basically been eliminated and replaced by Bluetooth and newer technologies.
ZigBee
ZigBee is an emerging short-range, low-power, low-rate, close-range wireless network technology. The basis for ZigBee is IEEE 802.15.4, a standard for the IEEE Wireless Personal Areas Working Group. However, IEEE 802.15.4 only deals with low-level MAC layers and physical layer protocols, so the ZigBee Alliance standardizes its network layer and API, and the Alliance is also responsible for its security protocols, application documentation, and marketing.
The ZigBee Alliance was established in August 2001 and is comprised of companies such as Invensys in the UK, Mitsubishi Electric in Japan, Motorola in the US, and Philips Semiconductors in the Netherlands. ZigBee and IEEE (Bluetooth), WiFi (wireless local area network) belong to the IEEE standard network protocol of the 2.4GHz frequency band, due to different performance positioning, their respective applications are different. 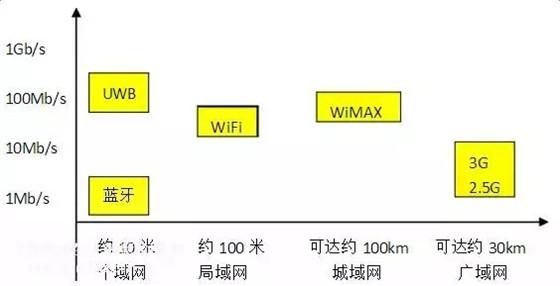
Bluetooth Bluetooth is a technical standard jointly proposed by Toshiba, Ericsson, IBM, Intel and Nokia in May 1998. As an open global specification for wireless data and voice communications, Bluetooth is based on low-cost, short-range wireless connectivity to establish a special connection between fixed and mobile device communication environments for short-range wireless transmission of data information. The essence of this is to establish a common public standard for the Radio Air Interface and its control software, so that the communication and the computer can be further combined, so that portable devices produced by different manufacturers can be connected without wires or cables. Interoperability and interoperability in close range. 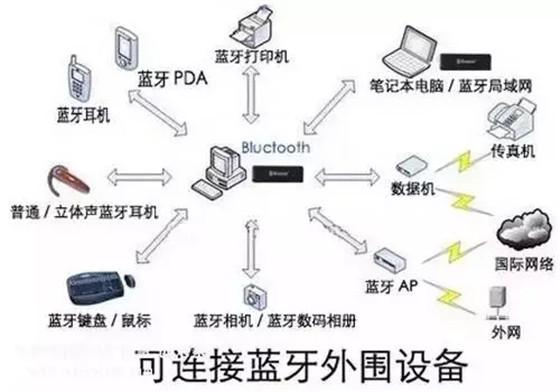
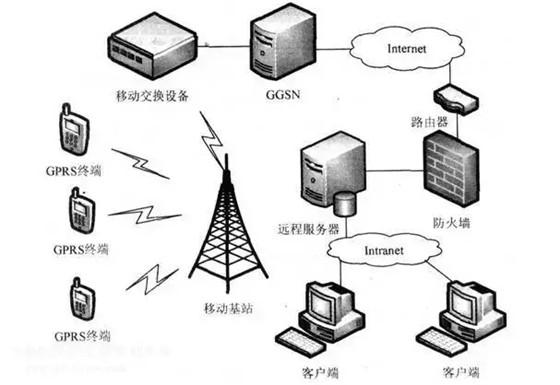
GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), using packet switching mode with mobility management and wireless access technology. GPRS can be said to be a continuation of GSM. GPRS is different from the previous method of continuously transmitting channels. It is transmitted in a packet type. Therefore, the user's cost is calculated based on the unit of transmission data. It is not the entire channel, which is theoretically cheaper. The transmission rate of GPRS can be increased to 56 or even 114Kbps. However, GPRS technology is not suitable for smart home use, mainly used in telecommunication networks. 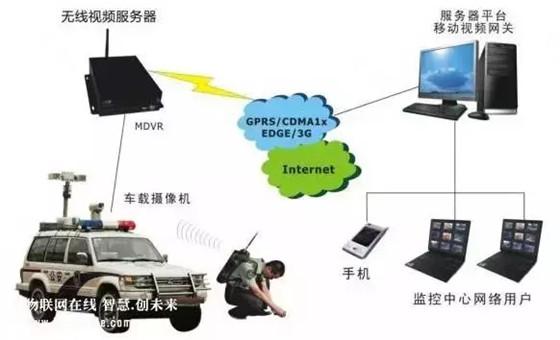
The third generation of mobile communication technology (3rd-generation, 3G) refers to cellular mobile communication technology that supports high-speed data transmission. 3G services can transmit both sound and data information at a rate of several hundred kbps or more.
There are currently four standards for 3G: CDMA2000 (US version), WCDMA (European version), TD-SCDMA (China version), WiMAX. In May 2000, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) identified three major wireless interface standards for WCDMA, CDMA2000 and TD-SCDMA, and wrote the 3G technical guidance document "International Mobile Communications Plan 2000". In 2007, WiMAX was also accepted as one of the 3G standards. 
The second generation mobile communication system mainly adopts the digital modulation method of time division multiple access (TDMA), which improves the system capacity and uses independent channel to transmit signaling, which greatly improves the system performance, but the system capacity of TDMA is still limited, and the handover performance is still limited. Still not perfect. The CDMA system shows great development potential due to its simple frequency planning, large system capacity, high frequency reuse coefficient, strong anti-multipath capability, good communication quality, soft capacity and soft handover.
4G
4G technology is also known as IMT-Advanced technology. The quasi-4G standard is the TD-LTE-Advanced title for the latest development of TD technology to 4G. There is not much disagreement about the core technologies that will be used in 4G. To sum up, there are five types of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technology, software radio, smart antenna technology, multiple input multiple output (MIMO) technology and IP-based core network.
Since the original purpose of researching 4G communication is to increase the rate of wireless access to the Internet by cellular phones and other mobile devices, the most impressive feature of 4G communication is its faster wireless communication speed. In addition, 4G has the advantages of wide network spectrum, flexible communication, high intelligent performance, good compatibility and low cost.
4G communication technology is not perfect, mainly reflected in the following aspects: First, the technical standards of 4G communication technology are difficult to unify. Second, the market promotion of 4G communication technology is difficult to achieve. Third, the supporting facilities of 4G communication technology are difficult to update. 
Wi-Fi is called Wireless Fidelity, also known as IEEE 802.11b. Its biggest advantage is that the transmission speed is high, it can reach 11Mb/s, and its effective distance is also long. It also works with various IEEE. 802.11 DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) devices are compatible.
The IEEE 802.11b wireless network specification is based on the IEEE 802.11a network specification. The maximum bandwidth is 11 Mb/s. When the signal is weak or interfered, the bandwidth can be adjusted to 5.5 Mb/s and 2 Mb/s. And 1Mb/s. The automatic adjustment of bandwidth effectively ensures the stability and reliability of the network. Wi-Fi wireless fidelity technology, like Bluetooth technology, is a short-range wireless technology used in offices and homes. The frequency band used is near 2.4GHz. This band is currently a wireless band that is not licensed. There are two standards that can be used. That is 802.11ay and 802.11b, 802.11g is the inheritance of 802.11b.
Its main characteristics are: high speed and high reliability. In the open area, the communication distance can reach 305m. In the closed area, the communication distance is 76-122m, which is convenient for integration with existing wired Ethernet, and the cost of networking is lower.
NB-IoT, the Narrow Band-Internet of Things, is a kind of Internet of Things technology with low cost, low power consumption and wide coverage. It is positioned at the carrier-grade, low-rate based on licensed spectrum. The networking market has broad application prospects. NB-IoT technology includes six major application scenarios, including location tracking, environmental monitoring, smart parking, remote meter reading, agriculture and animal husbandry. These scenes are precisely the scenes that are difficult to support with existing mobile communications. Market research firm Machina predicts that NB-IoT technology will cover 25% of IoT connections in the future.
NB-IoT is an important enhancement to 3GPP R13 Phase LTE with RF bandwidth as low as 0.18MHz. NB-IoT is a fusion of NB-CIoT and NB-LTE standards, balancing the interests of all parties and adapting to a wider deployment scenario. Among them, Huawei, Vodafone, Qualcomm and other companies support NB-CIoT; Ericsson, ZTE, Samsung, Intel, MTK and other companies support NB-LTE. Compared with the standard NB-IoT, NB-CIoT and NB-LTE have large differences, and the terminal cannot be upgraded smoothly. Some non-standard base stations even face the risk of network retreat.
With the continuous development of IoT technology and applications, wireless transmission protocols will usher in an unprecedented development, and its application in future intelligent systems will also show explosive growth. Understanding and mastering the core technologies such as ZigBee, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and RFID, and developing the corresponding interface and modularization of wireless communication products are definitely the correct means for enterprises to create business opportunities. Wireless transmission protocols have always been a key technology for the development of the Internet of Things, and will be the top priority in the future development of the Internet of Things.

What do you know about the types of wireless transmission protocols commonly used in smart locks and smart homes?
The concept of "Internet of Things" was first proposed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1999. The narrow Internet of Things refers to the "Internet of Things-Connected Objects". The connected subjects here include both items and items, as well as items to identification management equipment. .
0 times
Window._bd_share_config = { "common": { "bdSnsKey": {}, "bdText": "", "bdMini": "2", "bdMiniList": false, "bdPic": "", "bdStyle": " 0", "bdSize": "24" }, "share": {}, "image": { "viewList": ["qzone", "tsina", "tqq", "renren", "weixin"], "viewText": "Share to:", "viewSize": "16" }, "selectShare": { "bdContainerClass": null, "bdSelectMiniList": ["qzone", "tsina", "tqq", "renren" , "weixin"] } }; with (document) 0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0] || body).appendChild(createElement('script')).src = 'http://bdimg.share. Baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion=' + ~(-new Date() / 36e5)];
