A large class of alcohols and organic compounds is a compound in which a hydrogen atom in an aliphatic hydrocarbon, an alicyclic hydrocarbon or an aromatic hydrocarbon side chain is substituted with a hydroxyl group. Generally referred to as an alcohol, the hydroxyl group is attached to a saturated, sp3 hybridized carbon atom. If the hydroxyl group is bonded to the benzene ring, it is a phenol; if the hydroxyl group is linked to the sp2 hybridized olefinic carbon, it is an enol. The properties of phenols and enols are quite different from those of general alcohols.
A phenol having the general formula of ArOH is a type of aromatic compound in which a hydrogen on an aromatic hydrocarbon ring is substituted with a hydroxyl group (-OH). The simplest phenol is phenol. The phenolic compound refers to a compound formed by substituting a hydrogen atom on a benzene ring in an aromatic hydrocarbon with a hydroxyl group, and can be classified into a monohydric phenol and a polyhydric phenol according to the number of hydroxyl groups contained in the molecule.
Alcohols, Phenols, Phenolic Compounds And Derivatives Bulk Isopropyl Alcohol,Isopropyl Alcohol,Industrial Grade Methanol,Bulk Methanol 99% Jinan huijinchuan trading Co. LTD , https://www.hjcchemical.com






Application of low cost sand in the production of D30 cylinder block
D30 cylinder block belongs to Yuchai 4D series cylinder block, which is produced in our factory HWS static pressure molding line. Since the mass production of D30 cylinder block castings, casting defects such as sanding, sintering and veining in the ejector chamber and the water channel have been observed. Therefore, in order to ensure the quality of the D30 cylinder block ejector chamber and the water channel cavity, the ejector chamber core and the water channel core have been produced using high-cost white corundum composite sand. Corundum sand is obtained by pulverizing and washing high alumina bauxite (main component Al2O3) and melting it in an electric furnace at a high temperature of 2000-2400 °C. It has the characteristics of high refractoriness, stable volume at high temperature and not easy to crack. The corundum sand for casting is divided into white corundum sand and brown corundum sand. White corundum composite sand is made by mixing white corundum sand and ordinary silica sand in a certain proportion. The use of corundum sand as the casting core sand can reduce the defects such as sanding and sintering in the inner cavity of the casting, and it is not easy to have veins and improve the quality of the inner cavity of the casting. However, due to its relatively high price, the cost of castings is increased in batch production. In order to effectively control the cost, the author's foundry requires that the cost of core sand should be reduced without reducing the quality of the inner cavity of the casting. It is necessary to develop low-cost sand on the core of the D30 cylinder block and the water core.
According to the actual production conditions and process characteristics of our factory, the low-cost sand developed on the D30 cylinder block ejector core and water channel core is selected from large forest sand with moderate SiO 2 content and low mud content, and to reduce the casting cavity. Adhesives such as sand and veins are added to the Dalin sand to increase the amount of anti-fibration agent produced by a company.
First, the core sand performance comparison
Sand mixing process
White corundum composite cold core sand (see Table 1 for matching ratio) is obtained by mixing white corundum composite sand (see Figure 1) with resin for cold core box in a certain ratio for 10-20s.
D3 cylinder block ejector core and waterway core are produced by white corundum composite cold core sand. Casting ejector chamber and water channel inner cavity have less casting defects such as sanding, sintering and veining. This process has been applied to D30 cylinder block in batches.
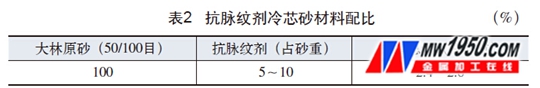
Low-cost sand, that is, anti-veining agent cold core sand (see Table 2 for matching ratio), is made by mixing large forest sand (see Figure 2) with resin and anti-veining additive (see Figure 3) at a certain ratio. . Due to the crystal transformation of SiO 2 under the action of high temperature molten iron, linear expansion occurs, which causes the sand core to crack into seams, and the castings have “vein vein†defects, and the anti-fibration agent can be used as a repellent additive in the core sand. Can reduce the expansion stress of the sand core. Adding 5% to 10% of the anti-ageage agent to the core sand can effectively prevent the "veining" defects of the casting.
2. Core sand strength comparison
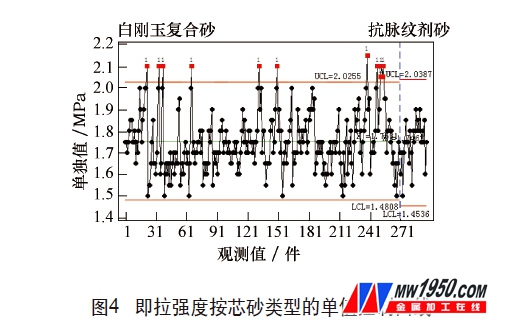
The performance of the two core sands was compared and analyzed from the two aspects of tensile strength and normal tensile strength. According to the data of the performance of the two core sands collected according to the mass production and test process, the distribution of the tensile strength and the normal tensile strength of the two core sands are obtained, as shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, respectively.
From the performance distribution range of the two core sands in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, the performance of the white corundum composite sand and the low cost sand core sand is equivalent.
Using low-cost sand to produce D30 cylinder body ejector core and water channel core, the sand core is full, and the core shooting process is normal, compared with the sand core produced by white corundum composite sand, as shown in Figure 6 ~ Figure 9, respectively.
Second, the casting quality comparison
Inner cavity cleanliness
The D30 cylinder block ejector core and water core are produced by low-cost sand test, and the core, lower core and pouring are carried out according to the mass production process. The cleanliness of the ejector chamber and the water channel cavity of the prototype is good, no bulk sand and veins appear, and the quality of the D30 cylinder ejector chamber and the water channel cavity produced by the white corundum composite sand are similar, as shown in Figure 10~ 13 is shown.
2. Casting size and scrap rate
Low-cost sand production D30 cylinder block ejector core and water channel core, the size of the corresponding position of the casting is marked, the results meet the casting dimensional accuracy requirements.
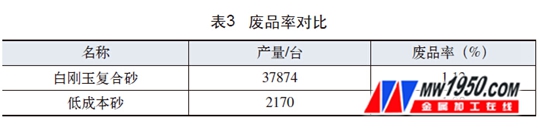
The number of D30 cylinder blocks produced during low-cost sand verification and the scrap rate were counted, and compared with the scrap rate of white corundum composite sand production castings, the use of low-cost sand production has no significant impact on the scrap rate of castings, see table 3.
Third, batch production verification and cost comparison
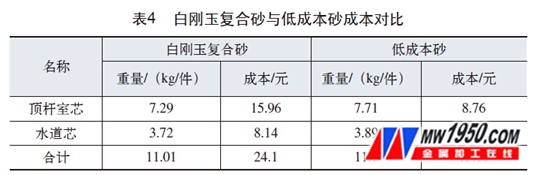
In the D30 cylinder block ejector core and water channel core, low-cost sand is used for mass production verification. The casting ejector chamber and the water channel cavity have no abnormal sand, sintering and vein defects. The cleanliness of the cavity meets the appearance quality requirements of the casting. And the quality of the casting cavity produced by the white corundum composite sand is equivalent. At the same time, the low-cost sand is obtained from the low-cost large forest sand and added with appropriate amount of anti-age agent, which reduces the cost of the D30 cylinder system core sand (see Table 4), thereby reducing the production of D30 cylinder block castings. cost.
Fourth, the discussion on the application mechanism of low cost sand
The low-cost sand developed by our factory is made by adding an appropriate amount of anti-age agent to Dalin sand. It can reduce the cost of core sand and reduce defects such as veins in the casting cavity. There are two basic reasons for the casting veins: one is the phase change of quartz stone at 573 °C, the volume expansion causes the surface of the sand core to crack into a seam; the second is that the sand core is surrounded by high temperature molten iron, which generates a large amount of gas and is difficult to discharge quickly. The instantaneous stress in the cavity is greater than the penetration resistance of the molten iron, and the molten metal penetrates into the entire section of the sand core through the crack or pore of the sand core to form a vein or permeable mechanical sand. Dalin sand contains more feldspar than sea sand. The feldspar softens and shrinks at 1200-1300 °C, which provides space for high-temperature expansion of silica sand and reduces the expansion and cracking of sand core. The main component of the anti-skew agent is a composite inorganic material, which can be used as a repellent additive in the core sand, which can reduce the expansion stress of the sand core and increase the thermal strength and thermoplasticity of the sand core. Adding an appropriate amount of anti-ageage agent to the core sand can effectively prevent the "veining" defects of the casting and has no effect on the size of the casting.
V. Conclusion
(1) The performance strength of the low-cost sand and white corundum composite sand production sand core is equivalent, and there is no significant difference in the quality of the casting cavity.
(2) The low-cost sand production process of D30 cylinder block ejector core and waterway core is feasible, and it can replace high-cost white corundum composite sand.
references
[1] Foundry Branch of China Mechanical Engineering Society. Casting Handbook: Modeling Materials [M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2002.
[2] Liu Hongxun. Characteristics and application of Dalinsha. Proceedings of the 5th High-level Forum of China Foundry Industry [C]. Nanjing. China Foundry Association, 2011.281-282.
About the author: Hu Shi'an, Huang Jinda, Guangxi Yuchai Machinery Co., Ltd.
Note: This article belongs to the Metal Processing Magazine, and may not be reproduced without authorization!
